CEO Elliot Mainzer’s recent Congressional testimony on grid reliability

CAISO President and CEO Elliot Mainzer was one of seven grid operators around the country asked to participate in a recent Congressional hearing before the House of Representatives Subcommittee on Energy, Committee on Energy and Commerce. The focus of the hearing was “Keeping the Lights On: Examining the State of Regional Grid Reliability”
With minor editing to reflect some updated numbers since the March 25 hearing, what follows is CEO Mainzer’s written testimony to the subcommittee. You can watch an archived recording of the hearing here.
Thank you for the opportunity to testify today. My name is Elliot Mainzer. I serve as President and Chief Executive Officer of the California Independent System Operator Corporation, commonly referred to as the CAISO.
The CAISO is a nonprofit, public-benefit corporation that does not own any generation or transmission assets. We play a number of key roles to ensure the grid is reliable, including transmission planning, overseeing interconnection of new resources, operation of electricity markets, and providing Reliability Coordinator services to 42 entities operating in the Western Interconnection. We do not operate a centralized capacity market but work with state and municipal entities to ensure adequate procurement and deployment of generation and storage resources.
Reliability
Like other regions of the country, California has faced extreme weather and other challenges, but the CAISO and our state partners have made major advances in reliability in recent years due to common sense approaches to expanding energy supply, efficiently interconnecting new resources, and proactively planning for transmission upgrades. New resources are coming online at a rapid pace.
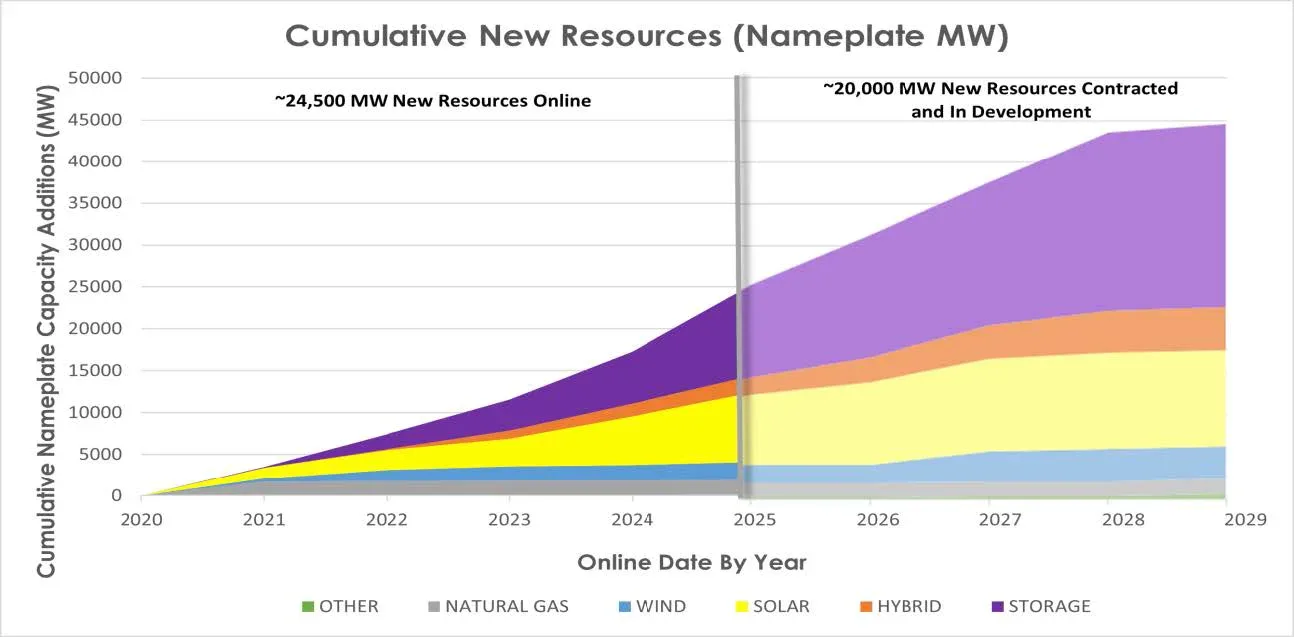
Since 2020, over 24 GW of new generation capacity has been added to the CAISO grid, including approximately 7 GW last year. This new capacity includes over 11 GW of battery storage. The CAISO relies on these new resources, as well as a diverse generation mix that includes solar, wind, geothermal, biogas, hydro, natural gas, and nuclear generation to maintain reliability.
During the next five years, we expect resource growth to continue to be comprised largely of battery storage, solar, and wind resources.
State-Driven Process
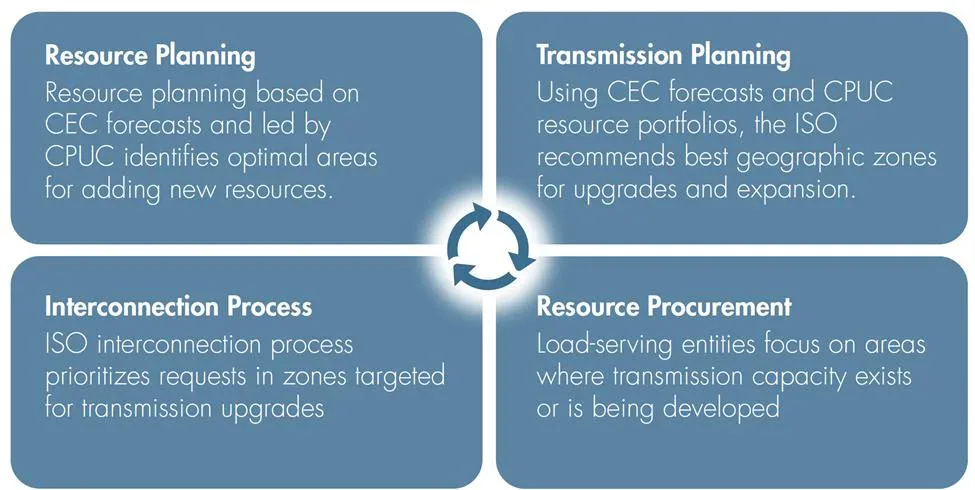
At the CAISO, we work to ensure safe and reliable service to electricity customers through collaboration with California’s state agencies and other local regulatory authorities. The CAISO, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC), and the California Energy Commission (CEC) have entered into a memorandum of understanding to help synchronize load forecasting, power and transmission planning, interconnection queuing and procurement of new resources.
This enhanced coordination has been essential to onboarding the thousands of megawatts of new generating capacity and battery energy storage that have come on line in recent years and will continue to guide our approach to ensuring reliability and resource adequacy in California.
The reliability of our grid has also been advanced by thoughtful and timely oversight by FERC. Last year, FERC approved a comprehensive set of interconnection queue reforms resulting from an extensive CAISO stakeholder process that was anchored in our approach to coordinated planning. Based on our implementation so far, we have observed a significant reduction in projects clogging our interconnection study process.
The CAISO’s 2024-2025 Transmission Plan included 31 new projects at an estimated cost of $4.8 billion to support the addition of more than 76 GW of new resources by 2039. We are also actively engaged in several inter-regional transmission projects that will access clean energy resources identified in the CPUC’s resource planning efforts that will also help deliver new generating resources and support reliability for utilities in other states.
Large Load Growth
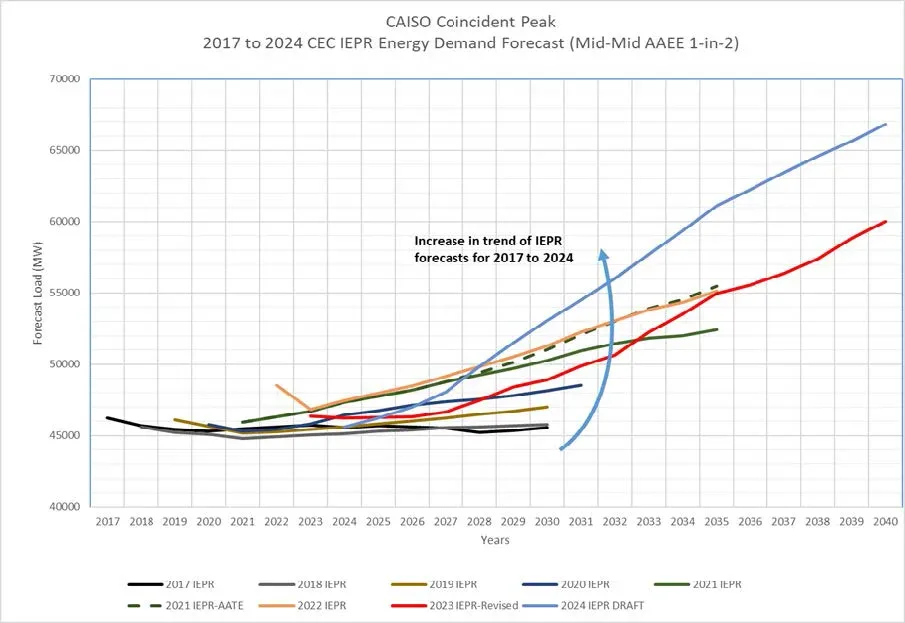
Electrification of transportation and buildings has been the primary driver of load growth to date within the CAISO’s footprint. The CEC’s latest demand forecast shows a 33% growth in peak demand over the next 10 years, and a 45% growth in peak demand over the next 15 years.
Currently, there is about 1 GW of data center load connected to the CAISO system. The CEC projects an increase in data center loads over the next 15 years, with a sharp increase projected to start around the 2028 timeframe. The CAISO is working diligently to serve emerging large electric loads within our footprint, including major enhancements to the transmission system in the Silicon Valley.
Reliability in the West is further enhanced by the success of the CAISO’s Western Energy Imbalance Market (WEIM), which has been in operation since 2014. Optimizing supply and demand in 15-minute and 5-minute intervals, WEIM today spans 22 market participants in ten states and leverages the significant transmission connectivity and resource diversity across parts of the West, which is particularly valuable during extreme weather events.
We are now working to extend a new day-ahead market platform to others in the West. Fully approved by FERC in 2024, the Extended Day-Ahead Market will expand the ability to optimize supply and demand in the day-ahead timeframe which will further enhance market efficiency and reliability and reduce costs to the ratepayers of participating utilities.
Looking Forward
The CAISO recognizes that our work continues in order to maintain the pace of new resource development to meet growing electric demands and state policy goals. We remain focused on implementing our coordinated planning and interconnection processes and extending our market service offerings to other entities across the West. We look forward to further engagement with the federal government to ensure reliability and cost savings for electricity consumers. Thank you again for the opportunity to be here this morning and that concludes my testimony.


